

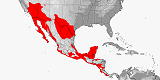

Related bibliographies:
Reptiles
 Lizards Lizards
 Eublepharidae Eublepharidae
Central America
North America





















































































































































































































































































































| |
Bibliography of the genus
Coleonyx (Banded Eyelid Geckos)

(Reptilia: Sauria: Eublepharidae)
Note:
In order to limit redundancy, relevant literature indexed in the related bibliographies in the left column may not have been included in this page. For a comprehensive search of literature, these bibliographies should therefore also be consulted.
Coleonyx in general
 |
Derbonne, W. 1934. Coleonyx in captivity. Copeia 1934: 191.
Dial, B.E.; Grismer, L.L. 1992. A phylogenetic analysis of physiological-ecological character evolution in the lizard genus Coleonyx and its implications for historical biogeographic reconstruction. Systematic Biology 41(2): 178-195.
Dixon, J.R. 1970. Coleonyx. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 95: 1-2.
Fritts, T.H.; Snell, H.L.; Martin, R.L. 1982. Anarbylus switaki Murphy: an addition to the herpetofauna of the United States with comments on relationships with Coleonyx. Journal of Herpetology 16(1): 39-52.
Grismer. L.L. 1983. A reevaluation of the North American gekkonid genus Anarbylus Murphy and its cladistic relationships to Coleonyx Gray. Herpetologica 39(4): 394-399.
Huey, R.B.; Niewiarowski, P.H.; Kaufmann, J.; Herron, J.C. 1989. Thermal biology of nocturnal ectotherms: is sprint performance of geckos maximal at low body temperatures? Physiological Zoology 62(2): 488-504.
Klauber, L.M. 1945. The geckos of the genus Coleonyx with descriptions of new subspecies. Transactions of the San Diego Society of Natural History 10(11): 133-215.
Kluge, A.G. 1962. Comparative osteology of the eublepharid lizard genus Coleonyx Gray. Journal of Morphology 110: 299-332.
Kluge, A.G. 1975. Phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary trends in the eublepharine lizard genus Coleonyx. Copeia 1975(1): 24-35.
Kratochvil, L.; Kubicka, L.; Landova, E. 2008. Does the mechanism of sex determination constrain the potential for sex manipulation? A test in geckos with contrasting sex-determination systems. Naturwissenschaften 95(3): 209-215.
Maderson, P.F.A. 1968. On the presence of 'escutcheon scales' in the eublepharine gekkonid Coleonyx. Herpetologica 24: 99-103.
Tashjian, J.H.; Scheidt, V. 1988. The eublepharine geckos. Jewels of the night. Vivarium (Lakeside) 1(3): 27-30.
Vergner, I. 1995. Geckos aus der Neuen Welt. Unterfamilie Eublepharinae. DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 48(8): 509-513.
|
Coleonyx brevis
 |
Baker, R.H.; Baker, M.W.; Johnson, J.D.; Webb, R.G. 1981. New records of mammals and reptiles from northwestern Zacatecas, Mexico. Southwestern Naturalist 25(4): 568-569.
Boyd, A.; Dayer, C.B.; Winter, K.E.; Schulte, J.J.; Smith, G.R.; Lemos-Espinal, J.A. 2010. Natural history notes: Coleonyx brevis (Texas Banded Gecko). Diet. Herpetological Review 41(3): 352.
Chrapliwy, P.S.; Fugler, C.M. 1955. Amphibians and reptiles collected in Mexico in the summer of 1953. Herpetologica 11: 121-128.
Dial, B.E. 1978. Aspects of the behavioral ecology of two Chihuahuan Desert geckos (Reptilia, Lacertilia, Gekkonidae). Journal of Herpetology 12(2): 209-216.
Dial, B.E. 1978. The thermal ecology of two sympatric, nocturnal Coleonyx (Lacertilia: Gekkonidae). Herpetologica 34(2): 194-201.
Dial, B.E.; Fitzpatrick, L.C. 1981. The energetic costs of tail autotomy to reproduction in the lizard Coleonyx brevis (Sauria: Gekkonidae). Oecologia (Heidelberg) 51(3): 310-317.
Dial, B.E.; Schwenk, K. 1996. Olfaction and predator detection in Coleonyx brevis (Squamata: Eublepharidae), with comments on the functional significance of buccal pulsing in geckos. Journal of Experimental Zoology 276(6): 415-424.
Dixon, J.R. 1970. Coleonyx brevis. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 88: 1-2.
Falko, J. 1973. The Texas banded gecko. Bulletin Canadian Amphibian and Reptile Conservation Society 11(2): 4-5.
Franklin, C.J.; Killpack, D.C. 2011. Natural history notes: Coleonyx brevis (Texas Banded Gecko). Invertebrate interactions. Herpetological Review 42(1): 93-94.
Johnson, J.D.; Johnson, G.W.; Riveroll, H. 2004. Natural history notes: Coleonyx brevis (Texas Banded Gecko). Tail regeneration. Herpetological Review 35(4): 388.
Kamees, L.K.; Burkett, D.W. 1995. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx brevis (Texas Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 26(1): 45.
Karges, J.P. 1978. Texas amphibians and reptiles: some new distributional records, part 1. Herpetological Review 9(4): 143-145.
Kratochvil, L.; Frynta, D. 2003. Production-growth model applied in eublepharid lizards (Eublepharidae, Squamata): Accordance between growth and metabolic rates. Folia Zoologica 52(3): 317-322.
Lazcano, D.; Pena, C.G. de la; Cataneda, G. 2006. Natural history notes: Coleonxy [Coleonyx] brevis (Texas Banded Gecko). Color pattern. Herpetological Review 37(2): 220.
Mulaik, S. 1935. Tail regeneration in Coleonyx brevis. Copeia 1935: 155-156.
Punzo, F. 1974. An analysis of the stomach contents of the gecko, Coleonyx brevis. Copeia 1974(3): 779-780.
Punzo, F. 1982. Clutch and egg size in several species of lizards from the desert southwest. Journal of Herpetology 16(4): 414-417.
Punzo, F. 2008. Chemosensory recognition of the marbled whiptail lizard, Aspidoscelis marmorata (Squamata, Teiidae) to odors of sympatric lizards (Crotophytus collaris, Coleonyx brevis, Eumeces obsoletus and Uta stansburiana) that represent different predation risk. Journal of Environmental Biology 29(1): 57-61.
Rösler, H. 1985. Texas Banded Gecko. Pflege und Zucht von Coleonyx brevis, Stejneger, 1893. Aquarium (Bornheim) 19(196): 537-540.
Rösler, H. 1986. Nachtrag zu meinem Artikel 'Texas banded gecko'. Pflege und Zucht von Coleonyx brevis, Stejneger, 1893. Aquarium (Bornheim) 20(205): 385.
Ruthven, D.C.; Kazmaier, R.T.; Moody, J.K. 1999. New county records from Dimmit and La Salle counties, Texas, USA. Herpetological Review 30(4): 238.
Schluter, U. 1999. Der Texanische Krallengecko. Vorkommen, Körpermerkmale sowie Pflege und Zucht von Coleonyx brevis. Aquarium (Bornheim) 357: 56-57.
Smith, H.M. 1933. On the relationships of the lizards Coleonyx brevis and Coleonyx variegatus. Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Sciences 36: 301-314.
Streicher, J.W.; Franklin, C.J.; Makowsky, R.A.; Cabrera-Guzman, E. 2010. Natural history notes: Thamnophis marcianus (Checkered Gartersnake). Diet. Herpetological Review 41(2): 238.
Werler, J.E. 1951. Miscellaneous notes on the eggs and young of Texan and Mexican reptiles. Zoologica (New York) 36: 37-48.
Williams, K.L.; Smith, H.M.; Chrapliwy, P.S. 1960. Turtles and lizards from northern Mexico. Transactions of the Illinois State Academy of Science 53(1/2): 36-45.
|
Coleonyx elegans
 |
Canseco-Marquez, L.; Gutiérrez-Mayén, G.; García-Vazquez, U.O.; Hernandez-Jimenez, C. 2004. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx elegans (Yucatan Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 35(3): 286.
Davis, W.B.; Dixon, J.R. 1961. Reptiles (exclusive of snakes) of the Chilpancingo region, Mexico. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 74: 37-56.
Duges, A. 1893. Coleonyx elegans, Gray. Naturaleza 2(2): 296-298.
Dunn, E.R.; Stuart, L.C. 1951. Comments on some recent restrictions of type localities of certain South and Central American amphibians and reptiles. Copeia 1951(1): 55-61.
Gray, R.; Strine, C.T. 2017. Herpetofaunal assemblages of a lowland broadleaf forest, an overgrown orchard forest and a lime orchard in Stann Creek, Belize. ZooKeys 707: 131–156.
Hernandez-Jimenez, C.A.; García-Vazquez, U.O. 2009. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx elegans (Yucatan Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 40(4): 451.
Hidalgo, H. 1981. Additions to the reptile fauna of El Salvador. Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science 84(1): 55-58.
Hofmann, T.; Kreuzer, M. 2017. Der Mexikanische und Mittelamerikanische Krallengecko - Coleonyx elegans und C. mitranus. Natur und Tier-Verlag, Münster. 62 pp.
Holfert, T. 1997. Coleonyx elegans Gray, 1845 (Sauria: Gekkonidae) - Haltung und Zucht im Terrarium. Sauria (Berlin) 19(3): 41-45.
Klauber, L.M. 1945. The geckos of the genus Coleonyx with descriptions of new subspecies. Transactions of the San Diego Society of Natural History 10(11): 133-215.
Kratochvil, L.; Frynta, D. 2003. Production-growth model applied in eublepharid lizards (Eublepharidae, Squamata): Accordance between growth and metabolic rates. Folia Zoologica 52(3): 317-322.
Monroy-Vilchis, O.; Domínguez-Vega, H.; Urbina, F. 2014. Primer registro de Coleonyx elegans nemoralis (Lacertilia: Eublepharidae) para el Estado de México, México. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad 85(1): 318-321.
Montalban Huidobro, C.A.; Juarez Orozco, H.; Castro-Franco, R. 2012. Nuevos registros del Gecko de Bandas de Colima Coleonyx elegans nemoralis Klauber 1945 (Sauria: Eublepharidae) en Morelos, México. Acta Zoologica Mexicana Nueva Serie 28(2): 479-481.
Neitman, K. 1984. Captive husbandry of the tuberculate geckos of the genus: Coleonyx. Annual Reptile Symposium on Captive Propagation and Husbandry Proceedings 7: 74-77.
Ottley, J.R. 1982. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx elegans nemoralis (Colima Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 13(3): 80.
Palacios-Aguilar, R.; Palacios-Hernandez, F. 2015. Primer registro de Coleonyx elegans nemoralis Klauber 1945 (Sauria: Eublepharidae) en una zona de transición de bosque de pino-encino y bosque de pino en Guerrero, México. Acta Zoologica Mexicana Nueva Serie 31(1): 134.
Ramirez-Bautista, A.; Flores-Villela, O.; Casas-Andreu, G. 1982. New herpetological state records for Mexico. Bulletin of the Maryland Herpetological Society 18(3): 167-169.
Reyes-Velasco, J.; Grünwald, C.I.; Jones, J.M.; Price, M.S.; Fisher, J.T. 2012. New distributional records for the herpetofauna of Mexico. Herpetological Review 43(3): 451-453.
Smith, P.W.; Burger, W.L. 1950. Herpetological results of the University of Illinois Field Expedition, Spring 1949. III. Sauria. Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Sciences 53: 165-175.
Trnik, M.; Albrechtova, J.; Kratochvil, L. 2011. Persistent effect of incubation temperature on stress-induced behavior in the Yucatan banded gecko (Coleonyx elegans). Journal of Comparative Psychology 125(1): 22-30.
|
Coleonyx fasciatus
 |
Brown, P.H.H.; Devender, T.R. van; Turner, D.S. 2016. Distribution notes: Coleonyx fasciatus (Boulenger, 1885). Mesoamerican Herpetology 3(4): 1045-1046.
Conant, R. 1965. Miscellaneous notes and comments on toads, lizards, and snakes from Mexico. American Museum Novitates 2205: 1-38.
Grismer, L.L. 1990. Coleonyx fasciatus. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 463: 1-2.
Lara-Resendiz, R.A.; Larrain-Barrios, B.C.; Felix-Burruel, R.E. 2017. Distribution notes: Coleonyx fasciatus (Boulenger, 1885). Mesoamerican Herpetology 4(4): 949-951.
Smith, H.S. 1989. The status of the lizard Coleonyx fasciatus and the biological species concept. Bulletin of the Maryland Herpetological Society 25(1): 22-24.
Taylor, E.H. 1935. Coleonyx fasciaius, a neglected species of Gecko. University of Kansas Science Bulletin 22: 203-205.
|
Coleonyx gypsicolus
 |
Grismer, L.L. 1999. An evolutionary classification of reptiles on islands in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Herpetologica 55(4): 446-469.
|
Coleonyx mitratus
 |
Angilletta, M.J.; Montgomery, L.G.; Werner, Y.L. 1999. Temperature preference in geckos: diel variation in juveniles and adults. Herpetologica 55(2): 212-222.
Bragg, W.K.; Fawcett, J.D.; Bragg, T.B.; Viets, B.E. 2000. Nest-site selection in two eublepharid gecko species with temperature-dependent sex determination and one with genotypic sex determination. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 69(3): 319-332.
Brongersma, L.D. 1954. On some lizards from the Republic of El Salvador. Proceedings Acad. Sci. Amst. 57C(2): 165-174.
Firneno, T.J.; Itgen, M.W.; Pereira-Pereira, F.M.; Townsend, J.H. 2016. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx mitratus (Central American Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 47(2): 257.
Hofmann, T.; Kreuzer, M. 2017. Der Mexikanische und Mittelamerikanische Krallengecko - Coleonyx elegans und C. mitratus. Natur und Tier-Verlag, Münster. 62 pp.
Kliment, P. 2011. Haltung und Biologie des Mittelamerikanischen Krallengeckos Coleonyx mitratus (Peters, 1863). Sauria (Berlin) 33(3): 3-18.
Köhler, G. 1998. Further additions to the known herpetofauna of Isla de Utila (Islas de la Bahia, Honduras) with notes on other species and a key to the amphibians and reptiles of the island (Amphibia, Reptilia). Senckenbergiana Biologica 77(2): 139-145.
Kratochvil, L.; Frynta, D. 2003. Production-growth model applied in eublepharid lizards (Eublepharidae, Squamata): Accordance between growth and metabolic rates. Folia Zoologica 52(3): 317-322.
Neitman, K. 1984. Captive husbandry of the tuberculate geckos of the genus: Coleonyx. Annual Reptile Symposium on Captive Propagation and Husbandry Proceedings 7: 74-77.
Peters, W.C.H. 1863. Über einen neuen Gecko, Brachydactylus mitratus aus Costa Rica. Monatsberichte der Königlich Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin 1863(January): 41-44.
Sunyer, J.; Martínez-Fonseca, J.G.; Salazar-Saavedra, M.; Arróliga, D.M.; Rivera Blandón, J.A.; Gutiérrez Rodríguez, A.A. 2017. Distribution notes: Coleonyx mitratus (Peters, 1863). Mesoamerican Herpetology 4(2): 450-456.
Tytle, T.; Stephens, P. 1993. Maintenance and breeding of the Central American banded gecko (Coleonyx mitratus). Vivarium (Lakeside) 5(2): 18-21.
|
Coleonyx reticulatus
 |
Davis, W.B.; Dixon, J.R. 1958. A new Coleonyx from Texas [C. reticulatus, sp. nov]. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 71: 149-152.
Dial, B.E. 1978. Aspects of the behavioral ecology of two Chihuahuan Desert geckos (Reptilia, Lacertilia, Gekkonidae). Journal of Herpetology 12(2): 209-216.
Dial, B.E. 1978. The thermal ecology of two sympatric, nocturnal Coleonyx (Lacertilia: Gekkonidae). Herpetologica 34(2): 194-201.
Dixon, J.R. 1970. Coleonyx reticulatus. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 89: 1.
Easterla, D.A.; Reynolds, R.C. 1975. Additional records and ecological notes on the reticulated gecko, Coleonyx reticulatus (Davis and Dixon), from the southern Trans-Pecos of southwestern Texas. Journal of Herpetology 9(2): 233-236.
Gallo, J.F.; Reese, K. 1978. Notes on the hatching of eggs and description of the hatchlings of reticulated gecko, Coleonyx reticulatus Davis & Dixon (Lacertilia: Eublepharidae). Southwestern Naturalist 23(2): 308-309.
Seifert, W.; Murphy, R.W. 1972. Additional specimens of Coleonyx reticulatus (Davis and Dixon) from the Black Gap Wildlife Management Area. Texas. Herpetologica 28(1): 24-26.
Seifert, W.; Rainwater, F.; Kasper, T. 1973. Signigicant range extensions with field and lab. notes for the reticulated gecko, Coleonyx reticulatus Davis & Dixon. Southwestern Naturalist 18(1): 101-103.
|
Coleonyx switaki
 |
Benes, E.S.; Muth, D.P. 1983. Another specimen of Anarbylus. Herpetological Review 14(4): 110.
Grismer, L.L. 1990. Coleonyx switaki. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 464: 1-2.
Grismer, L.L. 2001. Geographic variation of color pattern in peninsular populations of Coleonyx switaki (Squamata: Eublepharidae) from Baja California, México and southern California. Gekko 2(1): 14-19.
Grismer, L.L.; Hansen, R.W. 1994. Barefoot banded gecko. pp. 266-267. In: Thelander, C.G. & Crabtree, M. (eds.): Life on the edge: a guide to California's endangered natural resources: wildlife. Biosystems Books, Santa Cruz, California. 550 pp.
Grismer, L.L.; Ottley, J.R. 1988. A preliminary analysis of geographic variation in Coleonyx switaki (Squamata: Eublepharidae) with a description of an insular subspecies. Herpetologica 44(2): 143-154.
Murphy, R.W. 1974. A new genus and species of Eublepharine gecko (Sauria: Gekkonidae) from Baja California, Mexico. Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences 40(4): 87-92.
Putnam, R.W.; Murphy, R.W. 1982. Low metabolic rate in a nocturnal desert lizard, Anarbylus switaki Murphy (Sauria: Gekkonidae). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A Comparative Physiology 71(1): 119-123.
|
Coleonyx variegatus
 |
Autumn, K.; Farley, C.T.; Emshwiller, M.; Full, R.J. 1997. Low cost of locomotion in the banded gecko: a test of the nocturnality hypothesis. Physiological Zoology 70(6): 660-669.
Babb, R.D.; Brennan, T.C. 2013. Natural history notes: Coleonyx variegatus (Western Banded Gecko) and Rena humilis (Western Threadsnake). Attempted predation. Herpetological Review 44(3): 507-508.
Benefield, G.E.; Grimpe, R.D.; Olsen, E. 1981. Aspects of reproduction in Western banded geckos Coleonyx variegatus at Tulsa Zoo. International Zoo Yearbook 21: 83-87.
Bezy, R.L. 2010. Western Banded Gecko, Coleonyx variegatus (Baird, 1859 "1858"). Sonoran Herpetologist 23(7): 97-102.
Brattstrom, B.H. 1952. Diurnal activities of a nocturnal animal. Herpetologica 8(3): 61-63.
Brennan, T.C.; Feldner, M.J.; Koenig, H.F. 2002. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus (Western Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 33(4): 321.
Burke, R.L. 1994. Diurnal aggregation of banded geckos under field conditions. Southwestern Naturalist 39(3): 297-298.
Burke, R.L.; Yurewicz, K.L. 2012. Influence of size, loss of tail, and burst speed on risk of predation in the Banded Gecko (Coleonyx variegatus). Southwestern Naturalist 57(1): 87-91.
Bustard, R. 1962. The desert ground gecko. Aquarist and Pondkeeper 27: 166-167.
Bustard, R. 1965. A male Coleonyx variegatus variegatus (Baird), with two pairs of postanal spurs. British Journal of Herpetology 3: 208-209.
Bustard, R. 1967. Gekkonid lizards adapt fat storage to desert environments. Science (New York) 158: 1197-1198.
Carpenter, G.C.; Duvall, D. 1995. Fecal scent marking in the Western Banded Gecko (Coleonyx variegatus). Herpetologica 51(1): 33-38.
Clause, A.G.; House, D.J. 2016. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus variegatus (Desert Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 47(2): 257.
Conant, R. 1965. Miscellaneous notes and comments on toads, lizards, and snakes from Mexico. American Museum Novitates 2205: 1-38.
Conrad, P.M.; Bradley, P.V. 2009. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus (Western Banded Gecko). USA: Nevada. Herpetological Review 40(1): 112.
Cooper, W.E. 1998. Prey chemical discrimination indicated by tongue-flicking in the eublepharid gecko Coleonyx variegatus. Journal of Experimental Zoology 281(1): 21-25.
Cooper, W.E.; Caffrey, C.; Vitt, L.J. 1985. Aggregation in the banded gecko, Coleonyx variegatus. Herpetologica 41(3): 342-350.
Cooper, W.E.; Caffrey, C.; Vitt, L.J. 1985. Diel activity patterns in the banded gecko, Coleonyx variegatus. Journal of Herpetology 19(2): 308-311.
Dial, B.E. 1990. Predator-prey signals: chemosensory identification of snake predators by eublepharid lizards and its ecological consequences. Chemical Signals in Vertebrates 5: 555-565.
Dial, B.E.; Weldon, P.J.; Curtis, B. 1989. Chemosensory identification of snake predators (Phyllorhynchus decurtatus) by banded geckos (Coleonyx variegatus). Journal of Herpetology 23(3): 224-229.
Dixon, J.R. 1970. Coleonyx variegatus. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 96: 1-4.
Evans, K.J. 1965. Effects of cyclic light and temperature on the locomotor activity of the lizards Uta stansburiana and Colenyx variegatus. Dissertation Abstracts 26: 3541-3542.
Evans, K.J. 1967. Observations on the daily emergence of Coleonyx variegatus and Uta stansburiana. Herpetologica 23: 217-222.
Farley, C.T. 1997. Maximum speed and mechanical power output in lizards. Journal of Experimental Biology 200(16): 2189-2195.
Farley, C.T.; Emshwiller, M. 1996. Efficiency of uphill locomotion in nocturnal and diurnal lizards. Journal of Experimental Biology 199(3): 587-592.
Farley, C.T.; Ko, T.C. 1997. Mechanics of locomotion in lizards. Journal of Experimental Biology 200(16): 2177-2188.
Gardner, S.; Mendelson, J.R. 1999. Natural history notes: Coleonyx variegatus (Western Banded Gecko). Diet. Herpetological Review 30(4): 227.
Girard, F. 1994. Care and breeding of a North American gecko, Coleonyx variegatus, David 1859. Herptile 19(2): 67-70.
Girard, F. 1998. Maintien en captivite et reproduction de Coleonyx variegatus Gray, 1859. Bulletin de la Societe Herpetologique de France 84: 57-59.
Greenberg, B. 1943. Social behavior of the western banded gecko Coleonyx variegatus Baird. Physiological Zoology 16: 110-122.
Grismer, L.L. 1999. An evolutionary classification of reptiles on islands in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Herpetologica 55(4): 446-469.
Hague, M.T.J.; Routman, E.J. 2016. Does population size affect genetic diversity? A test with sympatric lizard species. Heredity 116(1): 92-98.
Hardy, R. 1944. Some habits of the banded gecko in southwestern Utah. Proceedings of the Utah Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters 21: 71-73.
Johnson, J.A.; Brodie, E.D. 1974. Defensive behaviour of the western banded gecko, Coleonyx variegatus. Animal Behaviour 22(3): 684-687.
Kaden, U. 1981. Der Gebänderte Krallengecko, Coleonyx variegatus. Aquarien Terrarien 28(8): 283-285.
Kingsbury, B.A. 1989. Factors influencing activity in Coleonyx variegatus. Journal of Herpetology 23(4): 399-404.
Kirkish, P.M.; Fobes, J.L.; Richardson, A.M. 1979. Spatial reversal learning in the lizard Coleonyx variegatus. Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society 13(4): 265-267.
Klauber, L.M. 1945. The geckos of the genus Coleonyx with descriptions of new subspecies. Transactions of the San Diego Society of Natural History 10(11): 133-215.
Lancaster, J.R.; Wilson, P.; Espinoza, R.E. 2006. Physiological benefits as precursors of sociality: why banded geckos band. Animal Behaviour 72(1): 199-207.
Moehn, L.D. 1962. A longevity record for Coleonyx variegatus. Herpetologica 18: 66-67.
Morris, B.R. 1991. Of lines and relationships: an accounting of Coleonyx variegatus subspecies. Dactylus 1(1): 20-25.
Murphy, R.W. 1974. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus. Mexico: Baja California del Sur: Isla Coronado. Herpetological Review 5(4): 107.
Parker, W.S. 1972. Aspects of the ecology of a Sonoran desert population of the western banded gecko, Coleonys variegatus (Sauria, Eublepharinae). American Midland Naturalist 88(1): 209-224.
Parker, W.S.; Pianka, E.R. 1974. Further ecological observations on the western banded gecko, Coleonyx variegatus. Copeia 1974(2): 528-531.
Persons, T.B.; Nowak, E.M. 2004. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus (Western Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 35(1): 81.
Price, A.H. 1980. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus bogerti. Herpetological Review 11(2): 38.
Putnam, R.W.; Murphy, R.W. 1982. Low metabolic rate in a nocturnal desert lizard, Anarbylus switaki Murphy (Sauria: Gekkonidae). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A Comparative Physiology 71(1): 119-123.
Ramirez-Bautista, A.; Perez Ramos, E.; Uribe-Pena, Z. 1989. New herpetological records from islands of the Gulf of California's Mexico. Herpetological Review 20(3): 76.
Reynoso, F. 1990. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus peninsularis (San Lucan Banded Gecko). Herpetological Review 21(1): 22.
Seib, R.L. 1978. Geographic distribution: Coleonyx variegatus peninsularis. Mexico: Baja California Sur: Isla Espiritu Santo. Herpetological Review 9(1): 22.
Smith, H.M. 1933. On the relationships of the lizards Coleonyx brevis and Coleonyx variegatus. Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Sciences 36: 301-314.
Smith, P.W.; Hensley, M.M. 1959. Notes on a small collection of amphibians and reptiles from the vicinity of the Pinacate lava cap in north-western Sonora, Mexico. Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Sciences 61: 64-76.
Vance, V.J. 1973. Temperature preference and tolerance in the gecko, Coleonyx variegatus. Copeia 1973(3): 615-617.
Vitt, L.J. 1977. Observations on clutch and egg size and evidence for multiple clutches in some lizards of southwestern United States. Herpetologica 33(3): 333-338.
Vitt, L.J.; Congdon, J.D.; Dickson, N.A. 1977. Adaptive strategies and energetics of tail autotomy in lizards. Ecology 58(2): 326-337.
Walde, A.D.; Currylow, A. 2015. Gopherus agassizii (Mojave Desert Tortoise) and Coleonyx variegatus variegatus (Desert Banded Gecko). Spring burrow cohabitation. Herpetology Notes 8: 501-502.
|
| | 















































































































































































|

