


Related bibliographies:
Reptiles
 Snakes Snakes
 Colubridae Colubridae
Asia
Malay Archipelago





















































































































































































































































































































| |
Bibliography of the genus
Fowlea (Fishing Keelbacks)

(Reptilia: Serpentes: Colubridae)
Note:
In order to limit redundancy, relevant literature indexed in the related bibliographies in the left column may not have been included in this page. For a comprehensive search of literature, these bibliographies should therefore also be consulted.
Fowlea in general
 |
Purkayastha, J.; Kalita, J.; Brahma, R.K.; Doley, R.; Das, M. 2018. A review of the relationships of Xenochrophis cerasogaster Cantor, 1839 (Serpentes: Colubridae) to its congeners. Zootaxa 4514(1): 126–136.
|
Fowlea flavipunctata
 |
Cheke, A.S. 1973. Snakes at Chiang Mai University. Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society 24(3-4): 469-471.
Cox, M.J. 1990. Life history notes: Xenocrophis flavipunctata (Common Keelback). Reproduction. Herpetological Review 21(1): 20-21.
Geissler, P.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Böhme, W. 2011. New records of snakes from Cat Tien National Park, Dong Nai and Lam Dong provinces, southern Vietnam. Bonn Zoological Bulletin 60(1): 9-16.
Pauwels, O.S.G. 2002. Natural history notes: Limnonectes limnocharis (Paddy Frog): Predation. Herpetological Review 33(2): 126.
Poo, S.; Low, M.R.; Devan-Song, A. 2016. Natural history notes: Xenochrophis flavipunctatus (Yellow-spotted Keelback Watersnake). Diet. Herpetological Review 47(2): 319.
Zug, G.R.; Blackburn, J.L.; Kyi, S.W. 2006. Checkered keelbacks (Xenochrophis - Reptilia: Serpentes: Natricidae) at the Moyingyi Wetland Bird Sanctuary, Myanmar. Hamadryad 30(1-2): 157-166.
|
Fowlea melanzosta
 |
Kopstein, F. 1930. Herpetologische Notizen. II. Oologische Beobachtungen an West-Javanischen Reptilien. Treubia 11: 301-307.
Kusuma, K.I.; Eprilurahman, R.; Vogel, G. 2010. First record of Xenochrophis melanzostus (Gravenhost, 1807) on Bali Island, Indonesia. Hamadryad 35(1): 113-115.
|
Fowlea piscator
 |
Aengals, R. 2011. A note on the food habits of the Checkered Keelback Water Snake Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider, 1799). Cobra (Chennai) 5(1): 14-15.
Aengals, R.; Rajarathinam, R. 1996. Breeding notes on Checkered Keelback watersnake in Madras Snake Park. Cobra (Madras) 23: 38.
Ananjeva, N.B.; Orlov, N.L. 1994. Caudal autotomy in colubrid snake Xenochrophis piscator from Vietnam. Russian Journal of Herpetology 1(2): 169-171.
Auffenberg, W. 1980. Autecological notes on Xenochrophis piscator (Reptilia: Serpentes) from Keoladeo Ghana Sanctuary. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences 6: 77-82.
Bhargava, R.N. 1969. A note on the catching device of the checkered keelback Natrix piscator (Schneider). Labdev 7B: 229.
Biswas, S. 1984. Some notes on the reptiles of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 81(2): 476-481.
Brooks, S.E.; Allison, E.H.; Reynolds, J.D. 2007. Vulnerability of Cambodian Water Snakes: initial assessment of the impact of hunting at Tonle Sap Lake. Biological Conservation 139(3-4): 401-414.
Brown, S.B. 1992. Microhabitat relations of some snakes and lizards in Tamil Nadu, south India. Hamadryad 17: 35-38.
Chacko, P.I. 1952. Piscivorous habit of the common watersnake, Natrix piscator Schneider. Proceedings Indian Sci. Congr. 38 [1952]: 232-233.
Cheke, A.S. 1973. Snakes at Chiang Mai University. Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society 24(3-4): 469-471.
Chhangani, A.K. 2005. Snake hunting fish at Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Rajasthan. Reptile RAP 7: 3.
Clark, R.J. 1990. A report on herpetological observations in Afghanistan. British Herpetological Society Bulletin 33: 20-42.
Daniels, R.J.R. 2002. Checkered keelback dies after swallowing a common Indian toad. Cobra (Chennai) 49: 15.
Dastidar, D.G.; Mani, S.D. 2008. Translocation of snakes from the NTPC campus at Alappuzha, Kerala, to the Konni Reserve Forest in Kerala. Cobra (Chennai) 2(1): 13-21.
Datta, A.K.; Khaledin, S. 2017. Frog leg: observations on an Indian Bull Frog swallowing an Asian Common Toad, and a Checkered Keelback on a Skipper Frog. Zoos' Print Magazine 32(6): 28-29.
Datta, A.K.; Khaledin, S. 2017. Observations on an Indian Bull Frog swallowing an Asian Common Toad, and a Checkered Keelback on a Skipper Frog. Zoo’s Print 32(6): 28-29.
Deshmukh, R.V.; Deshmukh, S.A.; Badhekar, S.A. 2018. Climbing behavior in a Checkered Keelback, Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider 1799), in central India. IRCF Reptiles & Amphibians 25(1): 46–47.
Deuve, J. 1963. Natrix piscator Schneider. Bulletin de la Société Royale des Sciences Naturelles du Laos 7: 23-35.
Deuve, J. 1963. Observations sur la tendance a la division de certaines plaques chez Natrix piscator piscator Schneider. Bulletin de la Société Royale des Sciences Naturelles du Laos 7: 37-44.
Farkas, B.; Fritz, U. 1999. Geographic distribution: Xenochrophis piscator (Checkered Keelback). Herpetological Review 30(3): 175.
Gairdner, K.G. 1915. Notes on the fauna and flora of Ratburi and Petchaburi districts (Part II). Journal of the Natural History Society of Siam 1(3): 131-156.
Ganesh, S.R.; Arumugam, M. 2016. Species richness of montane herpetofauna of southern Eastern Ghats, India: a historical resume and a descriptive checklist. Russian Journal of Herpetology 23(1): 7-24.
Gargi 2002. Interaction between Siberian crane Grus leucogeranus and checkered keelback snake Xenochrophis piscator in Keoladeo National Park, Bharatpur. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 99(1): 114-115.
Gay, T. 1976. Observations on a young chequered keelback snake (Xenochrophis piscator). Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 72(3) [1975]: 860-861.
Gupta, B.K. 1999. Euphlyctis hexadactylus (Lesson) feeding on Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider). Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 96(1): 158.
Haldar, C.; Pandey, R. 1987. Development of pineal gland in a tropical Indian water-snake, Natrix piscator. Archives d'Anatomie d'Histologie et d'Embryologie 70: 123-130.
Haque, M.N. 1989. Incident involving a snake and a purple heron. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 86(1): 95.
He, H. 1998. The current status of Xenochrophis piscator and conservation strategy. (In Chinese). Sichuan Journal of Zoology 17(2): 78.
Huang, W. 1997. Sexual size dimorphism in seven species of colubrid snakes in Taiwan. Bulletin of the National Museum of Natural Science (Taichung) 9: 107-116.
Husain, A. 2003. Reptilia. pp. 29-30. In: Director, Zoological Survey of India (ed.). Fauna of Asan Wetland (Dehra Dun Valley: Uttaranchal). [Wetland Ecosystem Series 5]. Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata. 56 pp.
Ingle, M. 2001. Notes on reptiles from Ujjain. Cobra (Chennai) 43: 14-15.
Ji, X.; Du, W.G.; Xu, X.F. 2001. [Influences of thermal and hydric environments on incubating eggs and resultant hatchlings in a colubrid snake (Xenochrophis piscator)]. (In Chinese, English summary). Acta Zoologica Sinica 47(1): 45-52.
Joseph, P.; Mathew, J.P.; Thomas, V.C. 2004. Locomotory behaviour in Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider), Naja naja (Linn) and Eryx johnii (Russell) under captive conditions. Cobra (Chennai) 56: 5-9.
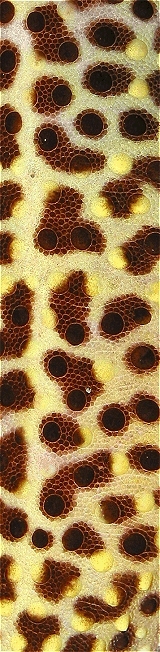
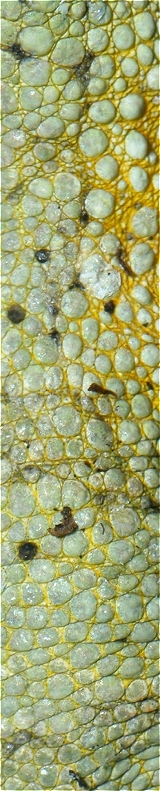
Joseph, P.; Mathew, J.P.; Thomas, V.C. 2007. Scale morphology, arrangement and micro-ornamentation in Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider), Naja naja (Linn), and Eryx johni (Russell). Zoos' Print Journal 22(12): 2909-2912.
Kalaichelvan, T.; Dubey, G.K. 2006. A case report of snake eating by rosy pelican (Pelecanus onocrotolus [onocrotalus]). Zoos' Print Journal 21(5): 15.
Kameswari, M.; Hanumanthu, D.; Narasimha Rao, L.; Raghu Ramulu, G. 1997. Neuroanatomy and distribution of esterases during growth in Proalaroides tropidonotis Vidyarthi, 1937 (Trematoda, Protodiplostomatidae). Rivista di Parassitologia 13(3) [1996]: 407-413.
Khaire, A.; Khaire, N.; Katdare, M. 1985. Observations on feeding, mating, egglaying and seasonal moulting of checkered keel back water snake (Xenochrophis piscator). The Snake 17(1): 25-30.
Khaire, N. 1977. Snake collecting in Matheran. Newsletter of the Madras Snake Park Trust 2(1): 10-11.
Khan, M.S. 1984. Validity of the natricine taxon Natrix sancti-johannis Boulenger. Journal of Herpetology 18(2): 198-200.
Khan, M.S. 1985. An interesting collection of amphibians and reptiles from Cholistan Desert, Punjab, Pakistan. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 82(1): 144-148.
Lu, H.L.; Hu, R.B.; Ji, X. 2009. The variance of incubation temperatures does not affect the phenotype of hatchlings in a colubrid snake, Xenochrophis piscator. Journal of Thermal Biology 34(3): 138-143.
Mao, J.J.; Cheng, Y.K.; Norval, G. 2004. A preliminary test and report on the efficiency of a new funnel trap for semi-aquatic snakes. Herpetological Review 35(4): 350-351.
Murphy, J.C.; Voris, H.K.; Karns, D.R.; Chan-Ard, T.; Suvunrat, K. 1999. The ecology of the water snakes of Ban Tha Hin, Songkhla Province, Thailand. Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society 47(2): 129-147.
Nareshwar, E.K. 2002. Rat snake feeding on Water Snake. Cobra (Chennai) 47: 17-18.
Norval, G.; Mao, J.J.; Huang, S.C.; Hou, C.; Lee, J. 2010. Xenochrophis piscator (Checkered Keelback): predation. Herpetological Bulletin 112: 39-41.
Pal, A.; Dey, S.; Roy, U.S. 2012. Seasonal diversity and abundance of herpetofauna in and around an industrial city of West Bengal, India. Journal of Applied Sciences in Environmental Sanitation 7(4): 281-286.
Parmar, D.S. 2018. Notes on the Checkered Keelback, Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider 1799), in Gujarat, India. IRCF Reptiles & Amphibians 25(2): 115–119.
Patel, K.; Patel, K.; Patel, H. 2017. Natural history notes: Xenochrophis piscator (Checkered Keelback). Diet and mortality. Herpetological Review 48(4): 869.
Petzold, H.G. 1963. Im Tierpark Berlin 1958 erstmalig gehaltene Tierformen. Mitt. aus dem Tierpark Berlin 1(4): 177-202.
Phansalkar, P.U.; Gowande, G.G. 2017. Climbing behavior in the Checkered Keelback or Asiatic Water Snake Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider, 1799) (Colubridae: Natricinae) in the Western Ghats, India. Russian Journal of Herpetology 24(1): 73-74.
Pillai, N.G. 1942. The number of eggs in the clutch of the checkered water-snake (Nerodia piscator). Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 48: 108-109.
Prakash, V.; Nanjappa, C. 1988. An instance of active predation by scavenger vulture (Neophron percnopterus ginginianus) on checkered keelback watersnake (Xenochrophis piscator) in Keoladeo National Park, Bharatpur, Rajasthan. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 85(2): 419.
Prater, S.H. 1927. Large brood of eggs of the checkered water snake Nerodia piscator. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 32: 225.
Rahman, S.C.; Opu, W.I.; Das, K.R. 2012. Natural history notes: Xenochrophis piscator (Checkered Keelback). Diet and foraging behavior. Herpetological Review 43(2): 352.
Sharma, B.D.; Sharma, T. 1976. Some ecological notes on Xenocrophis piscator (Serpentes: Colubridae) in the Poonch Valley, Jammu and Kashmir, India. British Journal of Herpetology 5(7): 560-561.
Sharma, S. 2004. Group hunting and mass feeding by checkered keel-back Water Snake (Xenochrophis piscator) in Shipra River. Reptile RAP 6: 10.
Sharma, S.K. 2000. Drought and reptiles: an experience in Rajasthan. Cobra (Chennai) 40: 9-10.
Simon, E.S. 1942. Notes on the breeding habits of some snakes. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 43(3): 533-534.
Singh, K.S.; Thapliyal, J.P. 1973. Twinning in the checkered water snake, Natrix piscator. Herpetologica 29(1): 19-20.
Singh, U.; Nath Mehrotra, P. 1988. Morphophysiology of the hemipenis in Natrix piscator (Reptilia, Ophidia). Indian Zoologist 12(3-4): 275-278.
Srivastava, P.C.; Thapliyal, J.P. 1966. The male sexual cycle of the chequered water snake, Natrix piscator. Copeia 1965(4) [1966]: 410-415.
Stumpel, A.H.P. 1981. Water snake (Xenochrophis piscator) imitates cobra. (Reptilia: Serpentes: Colubridae). Salamandra 17(3-4): 203-204.
Sudasinghe, B.S.A.T.H.; Kusuminda, T.G.T. 2012. Eine Beobachtung von Xenochrophis cf. piscator (Reptilia: Natriciidae) beim Erbeuten von Polypedates cruciger-Eiern (Amphibia: Rhacophoridae) in Sri Lanka. Sauria (Berlin) 34(2): 56-58.
Talukdar, S.K. 1977. A case of anterior dichotomy in a colubrid snake, Xenochrophis piscator (Schneider) (Reptilia: Serpentes: Colubridae). Science and Culture 43(12): 538-539.
Talukdar, S.K.; Sanyal, D.P.; Duttagupta, B. 1990. Rediscovery of holotype of Tropidonotus striolatus Blyth, 1868 (Serpentes: Colubridae) in the collection of the Zoological Survey of India. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 86(3) [1989]: 462-463.
Thite, V.K.; Nerlekar, A.N. 2012. Checkered keelback water snake Xenochropis piscator (Schneider, 1799) in the diet of Garden Calotes Calotes versicolor (Daudin, 1802). Herpetology Notes 5: 518.
Underwood, G. 1947. Reptiles of Cocanada. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 46(4): 613-028.
Underwood, G. 1948. Note on variation in Natrix p. piscator Schneider. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 118: 360-363.
Venkateswarlu, T.; Pattanayak, J.G.; Nahar, S.C.; Mohapatra, A. 1995. On the collection of snakes from Mahanadi Estuary (Orissa, India). The Snake 27(1): 49-52.
Vogel, G.; Han-Yuen, H.K. 2010. Death feigning behavior in three colubrid species of tropical Asia. Russian Journal of Herpetology 17(1): 15-21.
Wall, F. 1900. Notes on the breeding of Tropidonotus piscator. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 13: 373-374.
Xu, S.; He, H.Y. 1998. A comparative study on the larynges of ten species of snakes. Zoological Research 19(1): 90-92.
Yin, F.Y.; Guo, Y.W.; Teng, S.P.; Mao, S.H. 1996. Fine structure of the tongue and anterior process of the sublingual plica in two species of colubrid water snakes, Xenochrophis piscator and Enhydris chinensis. Herpetologica 52(2): 205-216.
Zug, G.R.; Blackburn, J.L.; Kyi, S.W. 2006. Checkered keelbacks (Xenochrophis - Reptilia: Serpentes: Natricidae) at the Moyingyi Wetland Bird Sanctuary, Myanmar. Hamadryad 30(1-2): 157-166.
|
Fowlea punctulata
 |
Pauwels, O.S.G.; David, P.; Nutphand, W.; Chimsunchart, C. 2002. First record of Xenochrophis punctulatus (Günther, 1858) (Serpentes: Colubridae: Natricinae) from Thailand. Hamadryad 26(2) "2001": 247-252.
Pauwels, O.S.G.; Sumontha, M.; David, P. 2004. Geographic distribution: Xenochrophis punctulatus (Spotted Keelback Water Snake). Herpetological Review 35(3): 294.
Sanyal, D.P.; Gayen, N.C. 2006. Reptilia. pp. 247-284. In: Alfred, J.R.B. (ed.). Fauna of Arunachal Pradesh. Part 1. State Fauna Series 13. Zoological Survey of India, Calcutta. 396 pp.
|
Fowlea schnurrenbergeri
 |
Mohapatra, P.P.; Dutta, S.K.; Parida, S.P. 2010. Report of Xenochrophis schnurrenbergeri Kramer, 1977 (Serpentes: Natricidae) from Orissa, India. Russian Journal of Herpetology 17(2): 94-96.
Purkayastha, J.; Das, M.; Sengupta, S.; Dutta, S.K. 2010. Notes on Xenochrophis schnurrenbergeri Kramer, 1977 (Serpentes: Colubridae) from Assam, India with some comments on its morphology and distribution. Herpetology Notes 3: 175-180.
|
| | 















































































































































































|

