

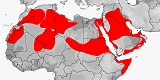

Related bibliographies:
Reptiles
 Lizards Lizards
 Agamidae Agamidae
Africa
Middle East





















































































































































































































































































































| |
Bibliography of the genus
Uromastyx (Western Spiny-tailed Agamas)

(Reptilia: Sauria: Agamidae)
Note:
In order to limit redundancy, relevant literature indexed in the related bibliographies in the left column may not have been included in this page. For a comprehensive search of literature, these bibliographies should therefore also be consulted.
Uromastyx in general
 |
Amer, S.A.M.; Kumazawa, Y. 2005. Mitochondrial DNA sequences of the Afro-Arabian spiny-tailed lizards (genus Uromastyx, family Agamidae): phylogenetic analyses and evolution of gene arrangements. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 85(2): 247-260.
Ananjeva, N.B.; Dujsebayeva, T.N.; Joger, U. 2001. Morphological study of the squamate integument: more evidence for the metataxon status of Leiolepidinae. Journal of Herpetology 35(3): 507-510.
Bertoni, R. 1995. Mastigures: spinytail agamids of the genus Uromastyx. Reptile & Amphibian Magazine 1995(September-October): 22-28, 30-31.
Ching, O.O.; Chng, S.C.L. 2016. The use of spiny-tailed lizards Uromastyx spp. for medicinal purposes in Peninsular Malaysia. Traffic Bulletin 28(1): 35-40.
Cloudsley-Thompson, J.L. 1970. A new record of Uromastix in Sudan. British Journal of Herpetology 4: 177.
Cooper, J.S.; Poole, D.F.G. 1973. The dentition and dental tissues of the agamid lizard, Uromastyx. Journal of Zoology (London) 169(1): 85-100.
Dyhrenfurth, A. 1977. Mein afrikanischer Dornschwanz. Aquarien- und Terrarien Magazin 30: 68-70.
Ensenyat, C. 1999. Uromastyx. A little-known genus? Reptilia (GB) 8: 26-32.
Frank, M. 2009. Dornschwanzagamen (Uromastyx): Neue Erkenntnisse für die Terrarienpraxis. Reptilia (D) 13(74): 70-75.
Harris, D.J.; Vaconcelos, R.; Brito, J.C. 2007. Genetic variation within African spiny-tailed lizards (Agamidae: Uromastyx) estimated using mitochondrial DNA sequences. Amphibia-Reptilia 28(1): 1-6.
Hart, H. 1975. Dornschwänze mögen Gelb. Aquarien Magazin 9(3): 100-101.
Hasi, M.; Lopez-Jurado, L.F.; Mateo, J.A.; Saint Andrieux, J.P.; Geniez, P. 1997. Nouvelles observations herpetologiques au Sahara Occidental, 3. Bulletin de la Societe Herpetologique de France 84: 33-38.
Herrel, A.; Castilla, A.M.; Al-Sulaiti, M.K.; Wessels, J.J. 2014. Does large body size relax constraints on bite-force generation in lizards of the genus Uromastyx? Journal of Zoology (London) 292(3): 170-174.
Hoser, R.T. 2014. A long overdue taxonomic rearrangement of the Uromastycinae (Squamata: Sauna: Agamidae). Australasian Journal of Herpetology 23: 54-64.
Husain, A. 2012. Distributional pattern of genus Uromastyx Merrem, 1820 (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae: Uromastycinae) in India, Arabia and Africa. Biological Forum, suppl. (Special Issue) 4(1): 114-122.
Joger, U. 1986. Phylogenetic analysis of Uromastyx lizards, based on albumin immunological distances. pp. 187-191, illustr. In: Rocek, Z. (ed.). Studies in herpetology. Proceedings of the European Herpetological Meeting (3rd Ordinary General Meeting of the Societas Europaea Herpetologica) Prague 1985. Charles University, Prague. 754 pp.
Johnson, J.D. 2006. Exotic animal care: spiny tailed lizards. Exotic DVM 8(4): 36-40.
Mateo, J.A.; Geniez, P.; Lopez-Jurado, L.F. 1998. Chorological analysis and morphological variations of saurians of the genus Uromastyx (Reptilia, Agamidae) in western Sahara. Description of two new taxa. Revista Espanola de Herpetologia 12: 97-109.
Moody, S.M. 1987. A preliminary cladistic study of the lizard genus Uromastyx (Agamidae, sensu lato), with a checklist and diagnostic key to the species. pp. 285-288. In: van Gelder, J.J.; Strijbosch, H. & Bergers, P.J.M. (eds.). Proceedings of the 4th Ordinary General Meeting of the Societas Europaea Herpetologica. Societas Europaea Herpetologica, Faculty of Sciences, Nijmegen. 473 pp.
Naldo, J.L.; Libanan, N.L.; Samour, J.H. 2009. Health assessment of a spiny-tailed lizard (Uromastyx spp.) population in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine 40(3): 445-452.
Naldo, J.L.; Samour, J.; Libanan, N. 2006. Preliminary report on the survey of the health status of the spiny-tailed lizard (Uromastyx sp) in Wrsan Farm, Al Ajban, Abu Dhabi, UAE. Wildlife Middle East News 1(3): 5.
Richter, W. 1954. Dornschwanzechsen. Kosmos (Stuttgart) 50: 144.
Robinson, P.L. 1976. How Sphenodon and Uromastyx grow their teeth and use them. Linnean Society Symposium Series 3: 43-64.
Seufer, H.; Kowalski, T.; Zilger, H.J. 2007. Die Dornschwanzagamen des Sultanats Oman. Draco 8(3) (31): 67-74.
Tamar, K.; Metallinou, M.; Wilms, T.; Schmitz, A.; Crochet, P.A.; Geniez, P.; Carranza, S. 2017. Evolutionary history of Spiny-tailed Lizards (Agamidae: Uromastyx) from the Saharo-Arabian region. Zoologica Scripta 47(2): 159-173.
Taylor, J.F. 2008. Uromastyx: A Complete Guide to Uromastyx. T.F.H. Publications, Neptune City, New Jersey. 128 pp.
Thatcher, T. 1987. Lizards in confinement and their husbandry. Part 2. ASRA (Association for the Study of Reptilia and Amphibia) Monographs 2(1): 47-53.
Thatcher, T. 1990. The ecology and captive maintenance of Uromastix species (family Agamidae). pp. 39-43. In: Coote, J. (ed.). Reptiles: Proceedings of the 1988 U.K. Herpetological Societies Symposium on Captive Breeding. British Herpetological Society, London. 108 pp.
Walls, J.G. 1996. Uromastyx & butterfly agamids. T.F.H. Publications, Inc., Neptune City, New Jersey. 65 pp.
Watson, G. 1968. Notes on the care of mastigure lizards. Jersey Wildlife Preservation Trust Special Scientific Report 5: 48-50.
Wermuth, H. 1957. Dornschwänze. Aquarien und Terrarien (Leipzig) 4: 4.
Wilms, T. (ed.) 2007. Dornschwanzagamen. Draco 8(3) (31): 1-88.
Wilms, T. 1995. Dornschwanzagamen. Lebensweise, Pflege und Zucht. Herpeton, Offenbach. 130 pp.
Wilms, T. 1999. Das Fortpflanzungsverhalten der Uromastyx-Arten. Reptilia (D) 4(16): 34-37.
Wilms, T. 1999. Die Pflege und Vermehrung von Dornschwanzagamen im Terrarium. Reptilia (D) 4(16): 25-29.
Wilms, T. 1999. Dornschwanzagamen. Reptilia (D) 4(16): 18-24.
Wilms, T. 2001. Dornschwanzagamen. Lebensweise, Pflege, Zucht. Herpeton, Offenbach. 142 pp.
Wilms, T. 2002. Habits, care, and breeding of spiny-tailed agamas. (The Uromastyx-ocellata complex as an example). Reptilia (GB) 21: 19-29.
Wilms, T. 2002. Uromastyx, spiny-tailed agamas. Reptilia (GB) 21: 12-18.
Wilms, T. 2002. Uromastyx: reproductive behavior. Reptilia (GB) 21: 30-33.
Wilms, T. 2005. Uromastyx: Natural History, Captive Care, Breeding. Herpeton, Offenbach. 143 pp.
Wilms, T. 2007. Dornschwanzagamen der Gattung Uromastyx - Einführung in Taxonomie und Ökologie einer auf Wüsten spezialisierten Echsengruppe. Draco 8(3) (31): 4-19.
Wilms, T. 2007. Unternehmen "Dornschwanzagame": Das Reptilium-Freilandforschungsprojekt in Saudi-Arabien. Draco 8(3) (31): 45-53.
Wilms, T. 2007. Ursachen und Ausmass der Bedrohung von Dornschwanzagamen - Versuch einer Bestandsaufnahme. Draco 8(3) (31): 75-80.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2000. Zur Taxonomie und Verbreitung der Arten der Uromastyx-ocellata-Gruppe (Sauria: Agamidae). Zoology in the Middle East 21: 55-76.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2001. Revision der Uromastyx acanthinura - Artengruppe, mit Beschreibung einer neuen Art aus der Zentralsahara (Reptilia: Sauria: Agamidae). Zoologische Abhandlungen (Dresden) 51(1): 73-104.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2007. Review of the taxonomy of the spiny-tailed lizards of Arabia (Reptilia: Agamidae: Leiolepidinae: Uromastyx). Fauna of Arabia 23: 435-468.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W.; Wagner, P.; Lutzmann, N.; Schmitz, A. 2009. On the phylogeny and taxonomy of the genus Uromastyx Merrem, 1820 (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae: Uromastycinae) - resurrection of the genus Saara Gray, 1845. Bonner Zoologische Beiträge 56(1-2): 55-99.
Wilms, T.; Mueller, H.D.; Loehr, B. 2002. Bunte Juwelen im Terrarium - Erfahrungen bei der langjährigen Pflege und Vermehrung von Uromastyx ornata (Heyden, 1827) bis zur F2-Generation. Draco 3(2) (10): 41-49.
Wilms, T.; Stassen, B.; Oppermann, A.; Petri, C. 2007. Ein Beitrag zur artgerechten Einrichtung und Beleuchtung von Terrarien für die Haltung von Dornschwanzagamen. Draco 8(3) (31): 20-29.
Wright, K. 2006. Working with Uromastyx lizards. p. 1692. In: Anononymous. Proceedings of the North American Veterinary Conference. Volume 20. January 7-11, 2006. Orlando, Florida. Small animals and exotics edition. Book 2. North American Veterinary Conference, Gainesville. pp. 887-1803.
|
Uromastyx acanthinura
 |
Berec, M.; Stara, Z.; Polakova, S. 2014. Relation between body-size and thermoregulation behavior: postprandial thermophily in Spiny-tailed Agama, Uromastyx acanthinura Bell. Polish Journal of Ecology 62(1): 139-145.
Böhme, W. 1978. Zur Herpetofaunistik des Senegal. Bonner Zoologische Beiträge 29(4): 360-417.
Borchert, U. 1971. Zur Haltung von Dornschwanz (Uromastyx acanthinurus) und Blauzungenskink (Tiliqua scincoides). DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 24: 348-351.
Brendel, H. 1959. Meine afrikanischen Dornschwänze (Uromastix acanthinurus). DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 12: 373-375.
Brendel, H. 1978. Eine Dornschwanz-Agame legt Eier. DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 31(9): 318-320.
Dubuis, A.; Faurel, L.; Grenot, C.; Vernet, R. 1971. Sur le régime alimentaire du lézard saharien Uromastix acanthinurus Bell. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances Academie des Sciences Paris (Ser. D) 273D: 500-503.
George, W. 1986. The thermal niche: desert sand and desert rock. Journal of Arid Environments 10(3): 213-224.
Grenot, C. 1967. Observations physico-ecologiques sur thermoregulation dans le lezard agamid Uromastix acanthinurus, Bell. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France 92: 51-66.
Grenot, C. 1968. Étude comparative de la resistance et a la chaleur d'Uromastix acanthinurus et de Varanus griseus. Terre et Vie 1968(4): 390-409.
Grenot, C. 1968. Sur l'excretion nasale de sels chez le lezard saharien: Uromastyx acanthinurus. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. Paris (D) 266: 1871-1874.
Grenot, C. 1969. Sur la regime alimentaire de la vipère a cornes. Science et Nature (Paris) 96: 21-24.
Grenot, C. 1974. Polymorphisme chromatique du lezard Agamide Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell dans les populations du Sahara Nord Occidental. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France 99: 153-164.
Grenot, C. 2001. Adaptation des petits vertebres aux conditions arides du Sahara. Bulletin de la Societe Zoologique de France 126(1-2): 129-167.
Grenot, C.; Loirat, F. 1973. L'activité et le comportement thermoregulateur du lezard Saharien Uromastix acanthinurus Bell. La Terre et la Vie (Paris) 27(3): 435-455.
Grenot, C.; Vernet, R. 1973. Sur une population d'Uromastix acanthinurus Bell isolée au milieu du Grand Erg occidental (Sahara algérien). Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances Academie des Sciences Paris (Ser. D) 276(8): 1349-1352.
Grimm, J. 1982. Nachzucht bei der nordafrikanischen Dornschwanzagame, Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell. Aquarien Terrarien 29(2): 64-69.
Grimm, J. 1986. Afrikanische Dornschwanzagamen, Uromastyx acanthinurus - langjährige Erfahrung bei Haltung und Nachzucht. Aquarien Terrarien 33(11): 384-386, 389.
Herrel, A.; Aerts, P.; Fret, J.; Vree, F. de 1999. Morphology of the feeding system in agamid lizards: ecological correlates. Anatomical Record 254(4): 496-507.
Herrel, A.; Aerts, P.; Vree, F. de 1998. Ecomorphology of the lizard feeding apparatus: a modelling approach. Netherlands Journal of Zoology 48(1): 1-25.
Herrel, A.; Timmermans, J.P.; Vree, F. de 1998. Tongue flicking in agamid lizards: morphology, kinematics, and muscle activity patterns. Anatomical Record 252(1): 102-116.
Herrel, A.; Vree, F. de 1999. Kinematics of intraoral transport and swallowing in the herbivorous lizard Uromastix acanthinurus. Journal of Experimental Biology 202(9): 1127-1137.
Hoch, R. 1951. Der afrikanische Dornschwanz (Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell). DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 1951: 20-22.
Hoffmann, P. 1987. Der Veränderliche Dornschwanz. Ist Uromastyx acanthinurus ein Anfängertier? Aquarium (Bornheim) 217: 369-371.
Ibrahim, A.; Ineich, I. 2005. Additional records to the herpetofauna of Nalut Province, Libya. African Herp News 38: 2-9.
Kolar, K. 1953. Die Sommerhaltung von Uromastyx acanthinurus und Varanus griseus im Freilandterrarium. DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 6: 186-188.
Kolar, K. 1957. Jugendentwicklung von Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell. Zoologische Garten (Leipzig) 23: 18-27.
Krabbe-Paulduro, U.; Paulduro, E. 1988. Pflege und Nachzucht der afrikanischen Dornschwanzagame Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell, 1825 (Sauria: Agamidae). Salamandra 24(1): 27-40.
Kwet, A. 2013. Die Nordafrikanische Dornschwanzagame. Terraria-Elaphe 2013(42): 56-57.
Matz, G. 1972. Terrariofilia Uromastix acanthinurus. Vida Acuatica 9: 310, 323-324.
Mertens, R. 1962. Bemerkungen über Uromastix acanthinurus als Rassenkreiss (Rept. Sauria). Senckenbergiana Biologica 43: 425-432.
Oliver, E. 1911. Variation de l'ecaillure chez Uromastix acanthinurus Bill. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France 36: 77-78.
Ortlepp-Schumacher, E.; Schumacher, R. 1988. Uromastix acanthinurus Bell 1825 - Nachzucht der Afrikanischen Dornschwanzagame. Sauria (Berlin) 10(4): 17-19.
Ortner, A. 1989. Pflegebedingungen und Nachzucht der Nordafrikanischen Dornschwanzagame (Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell, 1825). Herpetofauna (Weinstadt) 11(59): 11-16.
Ortner, A. 1989. Wiederholte Nachzucht der Nordafrikanischen Dornschwanzagame (Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell, 1825). Herpetofauna (Weinstadt) 11(63): 20-21.
Ortner, A. 1993. Erfolgreiche Nachzucht nordafrikanischer Dornschwanz-Agamen. DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 46(9): 576-577.
Pacyna, M. 1976. Veränderliche Doruschwänze, Uromastyx acanthinurus. Aquarium Aqua Terra 10(79): 36-38.
Pongratz, H. 1980. Eine Dornschwanz Geschichte. DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 33(11): 394-395.
Popp, B. 1934. Uromastix acanthinurus. Aquarium (Berlin) 1934: 104-106.
Popp, B. 1936. Uromastix acanthinurus. Aquarium (Berlin) 10: 75-76.
Richter, E. 1961. Zwei Arten Dornschwanz-Agamen, Uromastyx asmussi und Uromastyx acanthinurus, also "Haustiere". DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 14: 374-377.
Richter, E. 1966. Uromastyx acanthinurus 13½ Jahre in Gefangenschaft. DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 19: 25-27.
Robson, G.M.; Lambert, M.R.K. 1980. Observations on the insect food of some semi-desert lizards in southern Morocco. Journal of Arid Environments 3(2): 141-151.
Rode, E. 1950. Der Dornschwanz (Uromastyx acanthinurus Bell). Wochenschrift für Aquarien- und Terrarienkunde (Braunschweig) 44(8): 245-247.
Scortecci, G. 1940. Biologia del Tibesti. Ann. Mus. libico Stor. nat. 2: 257-275.
Stemmler-Diethelm, O. 1984. Afrikanische Dornschwänze Uromastyx acanthinurus (Bell 1825). Aquaria (St. Gallen) 31(5): 72-77.
Thatcher, T. 1981. Uromastix acanthinurus: a brief record of a trio of spiny-tailed agamids from Morocco, obtained October 1980. Rephiberary 48: 3.
Thatcher, T. 1992. The reproduction in captivity of the North African spiny-tailed lizard, Uromastyx acanthinurus. British Herpetological Society Bulletin 40: 9-13.
Thatcher, T. 1998. Herbivorous lizards with particular reference to the genus Uromastyx. Rephiberary 245: 2-5.
Thilenius, G. 1897. Der Farbenwechsel von Varanus griseus, Uromastix acanthurus und Agama inermis. Morphol. Jahrb. 7: 515-545.
Veraldi, M. 1955. Les lezards arboricoles. C. R. Soc. Sci. nat. Maroc 7: 112-113.
Vernet, R.; Lemire, M.; Grenot, C.J.; Francaz, J.M. 1988. Ecophysiological comparisons between two large Saharan lizards, Uromastix acanthinurus (Agamidae) and Varanus griseus (Varanidae). Journal of Arid Environments 14(2): 187-200.
Vogel, Z. 1980. Werden die nordafrikanischen Dornschwänze und Wüstenwarane das 20. Jahrhundert überleben? DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 33(1): 30-31.
Watson, G. 1969. Notes on the care of mastigure lizards Uromastix acanthinurus at Jersey Zoo. International Zoo Yearbook 9: 49-50.
Wheeler, S. 1990. Husbandry of the spiny-tailed agamas Uromastyx acanthinurus and U. aegyptius at Oklahoma City Zoo. International Zoo Yearbook 29: 70-74.
Wilms, T. 1995. Uromastyx acanthinura Bell 1825. Sauria (Berlin) 17(3): 333-340.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2001. Revision der Uromastyx acanthinura - Artengruppe, mit Beschreibung einer neuen Art aus der Zentralsahara (Reptilia: Sauria: Agamidae). Zoologische Abhandlungen (Dresden) 51(1): 73-104.
Wolf, J. 1972. Balzverhalten bei Uromastyx acanthinurus. Aquarien Terrarien Monatschrift für Ornithologie und Vivarienkunde 19(8): 279.
|
Uromastyx aegyptia
 |
Anonymous. 1987. Egyptian dabb lizards far afield. Israel Land and Nature 12(2): 77.
Abushama, F.T.; Cloudsley-Thompson, J.L. 1979. Desert arthropods of Kuwait and their distribution. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 114: 149-151.
Al-Hazmi, M.A. 2000. [Impact of urban development on behavioural ecology and density of dhab in Al-Gassim region, Saudi Arabia]. (In Arabic, English summary). Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research 18(3): 200-207.
Al-Hazmi, M.A. 2002. Feeding behaviour and food selection of dhab spiny-tailed lizard Uromastyx microlepis from wild vegetation. Journal of the Egyptian German Society of Zoology 37(A): 185-203.
Al-Hazmi, M.A.; Assaggaff, A.; Al-Anzy, A.A. 2005. Body temperature and behavioral thermoregulation of dhab spiny-tailed lizard Uromastyx microlepis in central Saudi Arabia. Journal of the Egyptian German Society of Zoology 47(A): 1-16.
Al-Johany, A.M.; Al-Saleh, S.S. 2000. Coexistence of Uromastyx aegyptius (Agamidae) and Leiurus quinquestriatus (Buthidae) under laboratory conditions. Pakistan Journal of Zoology 32(3): 189-191.
Alnaqeeb, M.A.; Al-Bustan, S.A.; Murad, N.Y.A. 2004. Effect of urban and industrial expansion on the genetic biodiversity of two desert animal species in Kuwait as determined by RAPD-PCR. Kuwait Journal of Science and Engineering 31(1): 15-32.
Al-Ogily, S.M.; Hussain, A. 1983. Studies on the ecology of the Egyptian spiny tailed lizard, Uromastix aegyptius (Forskål, 1775) in the Riyadh region, Saudi Arabia. Journal of the College of Science King Saud University 14(2): 341-351.
Al-Sadoon, M.K. 2001. Reproductive biology of Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis (Blandford, 1874) in the Central Region of Saudi Arabia. Journal of Union of Arab Biologists Cairo A Zoology 15: 1-14.
Al-Saleh, A.A.; Khan, M.A. 1986. Chromosomes of the spiny-tailed agamid lizard, Uromastix microlepis from Saudi Arabia with notes on chromosomes of Uromastix aegyptius. Canadian Society of Environmental Biologists Newsletter-Bulletin 29(1-2): 1-4.
Al-Saleh, S.A.; Al-Johany, A.M. 1995. Studies on the association between the spiny-tailed lizard Uromastyx aegyptius (Agamidae) and the black scorpion Androctonus crassicauda (Buthidae). Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research 13(3): 689-694.
Al-Shammari, A.M. 2012. Additional records of lizards in Ha'il Province, Saudi Arabia. Russian Journal of Herpetology 19(4): 287-291.
Amer, S.A.M.; Montaser, M.M.; Kumazawa, Y. 2011. Preliminary molecular variability within Uromastyx aegyptia microlepis (Reptilia: Agamidae) inhabiting Saudi Arabia. World Applied Sciences Journal 12(11): 1955-1961.
Arnold, E.N. 1980. The scientific results of the Oman flora and fauna survey 1977 (Dhofar). The reptiles and amphibians of Dhofar, southern Arabia. Journal of Oman Studies Special Report 2: 273-332.
Blanford, W.T. 1874. Description of two uromasticine lizards from Mesopotamia and southern Persia. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 1874: 656-661.
Bouskila, A. 1984. The burrows of the dabb-lizard, Uromastyx aegyptius. (Abstract). Israel Journal of Zoology 32(2-3): 151-152.
Bouskila, A. 1986. Habitat selection in the desert lizard Uromastyx aegyptius and its relation to the autecological hypothesis. pp. 119-128. In: Dubinsky, Z. & Steinberger, Y. (eds.). Environmental quality and ecosystem stability. Volume 3/A & 3/B. Proc. of the 3rd Int. Conference of the Israel Soc. for Ecology & Environmental Quality Sciences, Jerusalem, June 1-4, 1986. Bar-Ilan University Press, Ramat-Gan, Israel. 939 pp.
Bringsøe, H. 1998. Observations on growth and longevity in Uromastyx aegyptia (Forsskål, 1775) in the Negev Desert, southern Israel (Reptilia: Sauria: Agamidae). Faunistische Abhandlungen (Dresden) 21(Supplement): 19-21.
Castilla, A.M.; Richer, R.; Herrel, A.; Conkey, A.A.T.; Tribuna, J.; Al-Thani, M. 2011. First evidence of scavenging behaviour in the herbivorous lizard Uromastyx aegyptia microlepis. Journal of Arid Environments 75(7): 671-673.
Cloudsley-Thompson, J.L. 1983. Body temperature and defense in Uromastix microlepis. British Herpetological Society Bulletin 7: 77.
Cooper, W.E.; Al-Johany, A.M. 2002. Chemosensory responses to foods by an herbivorous acrodont lizard, Uromastyx aegyptius. Journal of Ethology 20(2): 95-100.
Cooper, W.E.; Al-Johany, A.M. 2005. Antipredatory threat displays and aggressive defenses by the acrodont lizard Uromastyx aegyptius (Acrodonta: Agamidae: Uromasticinae) when cornered and in crevices. Russian Journal of Herpetology 12(1): 69-73.
Corkill, N.L. 1928. Notes on the desert monitor (Varanus griseus) and the spiny-tailed lizard (Uromastix microlepis). Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 32(3): 608-610
Cunningham, P.L. 2000. Daily activity pattern and diet of a population of the spiny-tailed lizard, Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis, during summer in the United Arab Emirates. Zoology in the Middle East 21: 37-46.
Cunningham, P.L. 2001. Notes on the diet, survival rate, and burrow specifics of Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis from the United Arab Emirates. Asiatic Herpetological Research 9 [2000]: 30-33.
Cunningham, P.L. 2001. Spiny-tail lizard Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis diet - a study in the United Arab Emirates. Tribulus 11(2): 28-29.
Cunningham, P.L. 2007. Morphological characteristics of the Spiny-tailed Lizard, Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis (Agamidae), from the United Arab Emirates. Zoology in the Middle East 40: 105-107.
Cunningham, P.L. 2008. Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis (Blanford, 1874). Egyptian Spiny-tailed Lizard. African Herp News 46: 12-14.
Cunningham, P.L. 2009. Foraging behavior of the Egyptian spiny-tailed lizard Uromastyx aegyptia (Forskål, 1775). Herpetozoa 22(1-2): 91.
Cunningham, P.L. 2009. Seasonal variation in daily activity pattern in a population of spiny-tailed lizard, Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis, from the United Arab Emirates. Russian Journal of Herpetology 16(1): 6-10.
Dickson, V.P. 1966. Plants eaten by Uromastix microlepis Blanford and other notes on this lizard in eastern Arabia. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 62: 565-566.
Disi, A.M. 1991. A contribution to the herpetofauna of Jordan 4. Lizards of Jordan. Zoology in the Middle East 5: 25-35.
Disi, A.M.; Böhme, W. 1996. Zoogeography of the amphibians and reptiles of Syria, with additional new records. Herpetozoa 9(1-2): 63-70.
Dmi'el, R.; Rappeport, D. 1976. Effect of temperature on metabolism during running in the lizard Uromastix aegyptius. Physiological Zoology 49(1): 77-84.
Eissa, S.M. 1978. Studies on the energy metabolism of the desert lizard, Uromastyx microlepis, in relation to environmental temperature and body weight. Bulletin of the Faculty of Science Cairo University 47: 181-189.
Elmogy, M.; Sarhan, O.M.; Elgendy, A.M.; Alamodi, W.M. 2013. Morphological and molecular identification of some Uromastyx species (Reptilia; Agamidae) in Makkah, Saudi Arabia by forensically informative nucleotide sequencing (FINS) of 16S rRNA gene and electrophoretic protein patterns. Life Science Journal Acta Zhengzhou University Overseas Edition 10(4): 933-938.
Foley, W.J.; Bouskila, A.; Shkolnik, A.; Chosniak, I. 1992. Microbial digestion in the herbivorous lizard Uromastyx aegyptius (Agamidae). Journal of Zoology (London) 226(3): 387-398.
Haas, G. 1957. Some amphibians and reptiles from Arabia. Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences (Ser. 4) 29(4): 47-86.
Haas, G.; Battersby, J.C. 1959. Amphibians and reptiles from Arabia. Copeia 1959: 196-202.
Hassan, H.A. 1996. Chromosomal studies of four Egyptian lizards of the families Agamidae and Scincidae. Cytologia (Tokyo) 61(4): 443-455.
Henke, J.; Henke, H.; Nettmann, H.R.; Rykena, S. 1977. Bemerkungen zum Thema 'Ernährungsweise' von Uromastyx aegyptius (Reptilia, Sauria, Agamidae). Salamandra 13(2): 112-113.
Herrel, A.; Aerts, P.; Fret, J.; Vree, F. de 1999. Morphology of the feeding system in agamid lizards: ecological correlates. Anatomical Record 254(4): 496-507.
Ilani, G. 1982. Egyptian dabb lizards in loess habitats. Israel Land and Nature 7(2): 82.
Ilani, G.; Bouskila, A. 1982. Egyptian vultures and dabb lizards. Israel Land and Nature 8(1): 37.
Kevork, O.; Al-Uthman, H.S. 1972. Ecological observations on the Egyptian spiny-tailed lizard Uromastix aegyptius: 1. On food and feeding habits, with notes on the climate and vegetation of the study area. Bulletin Iraq Nat. Hist. Mus. 5(2): 26-44.
Khalil, F.; Hussein, M.F. 1962. Studies on the temperature relationships of Egyptian desert reptiles. 4. On the retention of heat of Uromastyx aegyptia, Agama pallida and Chalcides sepoides. Bull. Zool. Soc. Egypt 17: 80-88.
Khalil, F.; Hussein, M.F. 1963. Ecological studies in the Egyptian deserts. 3. Daily and annual cycles of Uromastyx aegyptia, Agama pallida and Chalcides sepoides with special reference to temperature and relative humidity. Proceedings of the Zoological Society U.A.R. 1: 93-108.
Kordges, T. 1998. Die Reptilienfauna des Thumamah Nature Park bei Riyadh, Saudi Arabien (Reptilia). Faunistische Abhandlungen (Dresden) 21(Supplement): 67-83.
Kowalski, T.; Seufer, H.; Zilger, H.J.; Grossmann, W.; Zwanzig, B.J. 2018. Die übersehenen Dornschwanzagamen östlich von Sur, Sultanat Oman. Sauria (Berlin) 40(3): 20-28.
Leshem, Y. 1980. ['Cactus garden' in the Eilat Mountains]. (In Hebrew, English summary). Torgos 1(1): 22, 49.
Mandaville, J.P. 1965. Plants eaten by Uromastyx microlepis Blanford and other notes on this lizard in eastern Arabia. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 61(10): 161-163.
Martin, J.; Castilla, A.M.; López, Pilar; Al-Jaidah, M.; Al-Mohannadi, S.F.; Al-Hemaidi, A.A.M. 2016. Chemical signals in desert lizards: Are femoral gland secretions of male and female spiny-tailed lizards, Uromastyx aegyptia microlepis adapted to arid conditions? Journal of Arid Environments 127: 192-198.
Monchot, H.; Bailon, S.; Schiettecatte, J. 2014. Archaeozoological evidence for traditional consumption of spiny-tailed lizard (Uromastyx aegyptia) in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Archaeological Science 45: 96-102.
Parker, H.W. 1930. Three new reptiles from southern Arabia. Annals and Magazine of Natural History (Ser. 10) 6: 594-598.
Robinson, M.D. 1995. Food plants and energetics of the herbivorous lizard, Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis, in Kuwait. Journal of the University of Kuwait (Science) 22(2): 255-262.
Roobas, B.; Feulner, G.R.; Thakur, Y. 2014. Bosk's Fringe-toed Lizard Acanthodactylus boskianus: follow-up study of a population in the Hajar Mountain foothills of the UAE. Tribulus 22: 35-40.
Ross, W. 1995. Body language in agamids of eastern Saudi Arabia. Tropical Fish Hobbyist 43(10): 124, 127-129, 131-133.
Sallam, F.A.E. 2005. Phylogenetic relationships among the Egyptian squamates (lizards and snakes) inferred from protein and isoenzyme characteristics. Journal of the Egyptian German Society of Zoology 48(C): 1-17.
Sallam, F.A.E.; Baker, H.S.A. 2006. Genetic variability of the agamid lizard Uromastyx aegyptia from Egypt and Saudi Arabia: biochemical and molecular evidence. Journal of the Egyptian German Society of Zoology 49(C): 141-161.
Seligmann, H. 1998. Evidence that minor directional asymmetry is functional in lizard hindlimbs. Journal of Zoology (London) 245(2): 205-208.
Soorae, P.S.; Howlett, J.; Samour, J. 2008. Use of transponders in the post-release monitoring of translocated spiny-tailed lizards (Uromastyx aegyptia microlepis) in Abu Dhabi Emirate, United Arab Emirates. Herpetological Bulletin 106: 1-3.
Throckmorton, G.S. 1976. Oral food processing in two herbivorous lizards, Iguana iguana (Iguanidae) and Uromastix aegyptius (Agamidae). Journal of Morphology 148(3): 363-390.
Throckmorton, G.S. 1980. The chewing cycle in the herbivorous lizard Uromastix aegyptius (Agamidae). Archives of Oral Biology 25(4): 225-233.
Wheeler, S. 1990. Husbandry of the spiny-tailed agamas Uromastyx acanthinurus and U. aegyptius at Oklahoma City Zoo. International Zoo Yearbook 29: 70-74.
Williams, J.B.; Shobrak, M.; Wilms, T.M.; Arif, I.A.; Khan, H.A. 2012. Climate change and animals in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 19(2): 121-130.
Williams, J.B.; Tieleman, B.I.; Shobrak, M. 1999. Lizard burrows provide thermal refugia for larks in the Arabian desert. Condor 101(3): 714-717.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2000. A new Uromastyx species from south-eastern Arabia, with comments on the taxonomy of Uromastyx aegyptia (Forskål, 1775) (Squamata: Sauria: Agamidae). Herpetozoa 13(3-4): 133-148.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W.; Wagner, P.; Lutzmann, N.; Schmitz, A. 2009. On the phylogeny and taxonomy of the genus Uromastyx Merrem, 1820 (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae: Uromastycinae) - resurrection of the genus Saara Gray, 1845. Bonner Zoologische Beiträge 56(1-2): 55-99.
Wilms, T.; Eid, E.K.A.; Al Johany, A.M.H.; Amr, Z.S.S.; Els, J.; Baha El Din, S.M.; Disi, A.M.; Sharifi, M.; Papenfuss, T.J.; Shafiei Bafti, S.; Werner, Y.L. 2012. Uromastyx aegyptia (errata version published in 2017). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012: e.T164729A115304711. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T164729A1071308.en.
Wilms, T.M.; Wagner, P.; Shobrak, M.; Lutzmann, N.; Böhme, W. 2010. Aspects of the ecology of the Arabian spiny-tailed lizard (Uromastyx aegyptia microlepis Blanford, 1875) at Mahazat as-Sayd protected area, Saudi Arabia. Salamandra 46(3): 131-140.
Wilms, T.M.; Wagner, R.; Shobrak, M.; Rödder, D.; Böhme, W. 2011. Living on the edge? - On the thermobiology and activity pattern of the large herbivorous desert lizard Uromastyx aegyptia microlepis Blanford, 1875 at Mahazat as-Sayd Protected Area, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Arid Environments 75(7): 636-647.
Yosef, R.; Yosef, N. 2010. Cooperative hunting in Brown-necked Raven (Corvus rufficollis [ruficollis]) on Egyptian Mastigure (Uromastyx aegyptius). Journal of Ethology 28(2): 385-388.
Zari, T.A. 1991. Effect of temperature on resting metabolic rate of the spiny tailed lizard, Uromastyx aegyptius microlepis. Journal of the Egyptian German Society of Zoology 4: 9-18.
|
Uromastyx alfredschmidti
 |
Joger, U.; Böhme, W. 2006. Uromastyx alfredschmidti. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2006: e.T61590A12502939. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2006.RLTS.T61590A12502939.en.
Sindaco, R.; Wilms, T.M.; Venchi, A. 2012. On the distribution of Uromastyx alfredschmidti Wilms and Böhme, 2000 (Squamata: Agamidae: Uromastycinae). Acta Herpetologica 7(1): 23-28.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2001. Revision der Uromastyx acanthinura - Artengruppe, mit Beschreibung einer neuen Art aus der Zentralsahara (Reptilia: Sauria: Agamidae). Zoologische Abhandlungen (Dresden) 51(1): 73-104.
|
Uromastyx benti
 |
Anderson, J. 1894. On two new species of agamoid lizards from the Hadramut, southeastern Arabia. Annals and Magazine of Natural History (Ser. 6) 14: 376-378.
Grossmann, W.; Zwanzig, B.M.; Kowalski, T.; Zilger, H.J. 2015. Anmerkungen zu Verbreitung, Lebensweise und Gefährdung der Jemen-Dornschwanzagame Uromastyx benti (Anderson, 1894) im Sultanat Oman. Sauria (Berlin) 37(3): 3-15.
Pierson, T.W.; Papenfuss, T.J. 2012. Natural history notes: Uromastyx benti (Bent's Spiny-tailed Lizard). Maximum elevation. Herpetological Review 43(3): 491.
Schätti, B. 1989. Amphibien und Reptilien aus der Arabischen Republik Jemen und Djibouti. Revue Suisse de Zoologie 96(4): 905-937.
Schätti, B.; Gasperetti, J. 1994. A contribution to the herpetofauna of southwest Arabia. Fauna of Saudi Arabia 14: 348-423.
Seufer, H.; Kowalski, T.; Prokoph, U.; Zilger, H.J. 1998. Erstnachweis von Uromastyx benti Anderson, 1894 für den Oman (Provinz Dhofar). Herpetofauna (Weinstadt) 20(114): 22-23.
Steindachner, F. 1899. Über eine neue Uromastix-Art, U. simonyi. Anz. Akad. Wiss. 1899: 143-144.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2000. Zur Taxonomie und Verbreitung der Arten der Uromastyx-ocellata-Gruppe (Sauria: Agamidae). Zoology in the Middle East 21: 55-76.
Wilms, T.; Sindaco, R.; Busais, S.M.S.; Mohammed, S.F. 2012. Uromastyx benti. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012: e.T199601A2605991. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T199601A2605991.en.
Zilger, H.J.; Zwanzig, B.M.; Grossmann, W.; Kowalski, T.; Ballandat, S. 2016. Neue Angaben zur Verbreitung der Jemen-Dornschwanzagame Uromastyx benti (Anderson, 1894) im Sultanat Oman. Sauria (Berlin) 38(4): 3-7.
|
Uromastyx dispar
 |
Gramentz, D. 1999. Zur Zwangsernährung von Uromastyx maliensis. Elaphe 7(3): 28-29.
Gramentz, D. 2001. Zum Komfortverhalten von Uromastyx dispar maliensis Joger & Lambert, 1996. Sauria (Berlin) 23(4): 37-39.
Hofstra, G. 2001. Spiny-tailed lizard from Mali: 'Uromastyx maliensis'. Podarcis 2(2): 44-53.
Mohammed, E.H.A.; Hammad, D.M. 2008. Notes on a sympatric population of two species of spiny-tailed lizards in Sudan: Uromastyx dispar Heyden, 1827, and U. ocellata Lichtenstein, 1823 (Sauria: Agamidae). Zoology in the Middle East 44: 51-56.
Ott, M. 2001. Anmerkungen zum Artikel von Rogner (2000) über die Mali-Dornschwanzagame. Aquarium (Bornheim) 380: 66-68.
Rogner, M. 2000. Die Mali-Dornschwanzagame. Zur Pflege und Zucht von Uromastyx maliensis. Aquarium (Bornheim) 377: 62-68.
Rogner, M. 2007. Die Mali-Dornschwanzagame, Uromastyx dispar maliensis. Draco 8(3) (31): 30-41.
Trape, J.F.; Trape, S.; Chirio, L. 2012. Lézards, crocodiles et tortues d'Afrique occidentale et du Sahara. IRD Éditions, Marseille. 503 pp.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2001. Revision der Uromastyx acanthinura - Artengruppe, mit Beschreibung einer neuen Art aus der Zentralsahara (Reptilia: Sauria: Agamidae). Zoologische Abhandlungen (Dresden) 51(1): 73-104.
Wilms, T.; Muller, H.D. 1998. Haltung und Zucht der Mali-Dornschwanzagame, Uromastyx maliensis Joger & Lambert, 1996. Herpetofauna (Weinstadt) 20(112): 25-33.
Wilms, T.; Ruf, D.; Loehr, B. 2003. Zur Haltung und Nachzucht zweier Taxa aus dem Uromastyx-acanthinura-Komplex: Uromastyx geyri Mueller, 1922 und Uromastyx dispar flavifasciata Mertens, 1962 (Reptilia: Agamidae: Leiolepidinae: Uromastyx). Draco 4(2) (14): 42-55.
|
Uromastyx geyri
 |
Guibé, J. 1950. Contribution a l'étude de l'Air (Mission L. Chopard et A. Villiers). Mem. Inst. Franc. Afr. Noire 10: 229-332.
Löhr, B. 2004. Die Geyrs Dornschwanzagame - Uromastyx geyri. Natur und Tier-Verlag, Münster. 64 pp.
Müller, L. 1922. Über eine neue Uromastix-Art aus Zentral-Sahara. Naturwiss. Beobachter (Frankfurt) 63: 193-202.
Müller, L. 1951. Aufstellung eines Neotypus von Uromastyx geyri L. Müller. Bonner Zoologische Beiträge 2(1-2): 109-111.
Turnbull, D. 2012. Breeding Uromastyx geyri. Herptile 37(4): 120-125.
Wilms, T.; Ruf, D.; Loehr, B. 2003. Zur Haltung und Nachzucht zweier Taxa aus dem Uromastyx-acanthinura-Komplex: Uromastyx geyri Mueller, 1922 und Uromastyx dispar flavifasciata Mertens, 1962 (Reptilia: Agamidae: Leiolepidinae: Uromastyx). Draco 4(2) (14): 42-55.
|
Uromastyx macfadyeni
 |
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2000. Zur Taxonomie und Verbreitung der Arten der Uromastyx-ocellata-Gruppe (Sauria: Agamidae). Zoology in the Middle East 21: 55-76.
|
Uromastyx nigriventris
 |
Bendami, S.; Znari, M.; Loulida, S. 2018. Inter-population and seasonal changes in food habits of the Moroccan Spiny-tailed lizard along an aridity gradient. Amphibia-Reptilia 39(3): 303–315.
Bruins, E. 2013. [The African spiny-tailed lizard in Morocco (3/3)]. (In Dutch). Aquarium (Hilversum) 83(1): 12-17.
Frank, M. 2012. Die marokkanische Dornschwanzagame - Uromastyx nigriventris. Natur und Tier-Verlag, Münster. 63 pp.
Pauwels, O.S.G.; Bonnin, J.L.; Sancho, V.; Wilms, T. 2017. Herpetoculture notes: Uromastyx nigriventris (Moroccan Spiny-tailed Lizard). Longevity. Herpetological Review 48(3): 569.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W.; Wagner, P.; Lutzmann, N.; Schmitz, A. 2009. On the phylogeny and taxonomy of the genus Uromastyx Merrem, 1820 (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae: Uromastycinae) - resurrection of the genus Saara Gray, 1845. Bonner Zoologische Beiträge 56(1-2): 55-99.
|
Uromastyx ocellata
 |
Evers, M. 2001. Haltung und Vermehrung der geschmückten Dornschwanzagame Uromastyx ocellata ocellata. Reptilia (D) 6(29): 56-61.
Frahm, S. 2006. Die Geschmückte Dornschwanzagame - Uromastyx ocellata. Natur und Tier-Verlag, Münster. 62 pp.
Kliche, B. 2004. Angaben zur Haltung, Zucht und Aufzucht von Uromastyx ocellata Lichentenstein, 1823. Sauria (Berlin) 26(3): 23-28.
Mohammed, E.H.A.; Hammad, D.M. 2008. Notes on a sympatric population of two species of spiny-tailed lizards in Sudan: Uromastyx dispar Heyden, 1827, and U. ocellata Lichtenstein, 1823 (Sauria: Agamidae). Zoology in the Middle East 44: 51-56.
Schätti, B.; Gasperetti, J. 1994. A contribution to the herpetofauna of southwest Arabia. Fauna of Saudi Arabia 14: 348-423.
Spawls, S. 2011. Uromastyx ocellata. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2011: e.T176223A7199657. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2011-1.RLTS.T176223A7199657.en.
Utong, J.A.M.; Abukashawa, S.M.A. 2013. Characterization of the agamid lizard genus Uromastyx from eastern Sudan based on morphology, karyotypes and mitochondrial DNA. Asian Herpetological Research 4(4): 268-281.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2000. Zur Taxonomie und Verbreitung der Arten der Uromastyx-ocellata-Gruppe (Sauria: Agamidae). Zoology in the Middle East 21: 55-76.
|
Uromastyx ornata
 |
Amer, S.A.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Wilms, T.M.; Shobrak, M.; Kumazawa, Y. 2012. Mitochondrial DNA variability within Uromastyx ornata philbyi (Agamidae: Squamata) from southwestern Saudi Arabia. Comparative and Functional Genomics 2012 (Article 851379): 1-8.
Bedir, M.A.; Boulos, R.; El Naggar, M.H. 1994. Ecological studies on the fauna of Wadi Sahab area in south Sinai with special reference to the agamid lizard Uromastyx ornatus. Journal of the Egyptian German Society of Zoology (A) 13: 105-120.
Elmogy, M.; Sarhan, O.M.; Elgendy, A.M.; Alamodi, W.M. 2013. Morphological and molecular identification of some Uromastyx species (Reptilia; Agamidae) in Makkah, Saudi Arabia by forensically informative nucleotide sequencing (FINS) of 16S rRNA gene and electrophoretic protein patterns. Life Science Journal Acta Zhengzhou University Overseas Edition 10(4): 933-938.
Evers, M. 2005. Haltung und Vermehrung der Bunten Dornschwanzagame. DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarien-Zeitschrift) 58(1): 24-28.
Evers, M. 2006. Die Bunte Dornschwanzagame - Uromastyx ornata. Natur und Tier-Verlag, Münster. 62 pp.
Haas, G.; Battersby, J.C. 1959. Amphibians and reptiles from Arabia. Copeia 1959: 196-202.
Molco, D. 2007. Beobachtungen zur Lebensweise von Uromastyx ornata in den Eilat-Bergen, Israel. Draco 8(3) (31): 54-60.
Parker, H.W. 1938. Reptiles and amphibians from the southern Hejaz. Annals and Magazine of Natural History (Ser. 11) 1: 481-492.
Petri, C. 2006. Haltung und Zucht der bunten Dornschwanzagame Uromastyx ornata (Heyden 1827) im Terrarium. Iguana Rundschreiben 19(2): 26-32.
Sallam, F.A.E.; Salama, A.B.H. 2006. Comparative biochemical and molecular investigations for the genetic variability of Uromastyx ornata (Agamidae: Reptilia) from Egypt and Saudi Arabia. Journal of the Egyptian German Society of Zoology 50(C): 217-237.
Schätti, B.; Gasperetti, J. 1994. A contribution to the herpetofauna of southwest Arabia. Fauna of Saudi Arabia 14: 348-423.
Seligmann, H. 1998. Evidence that minor directional asymmetry is functional in lizard hindlimbs. Journal of Zoology (London) 245(2): 205-208.
Vanderlinden, A. 1999. Notes on the captive breeding of ornate spiny-tailed lizards. Bulletin of the Chicago Herpetological Society 34(6): 154-155.
Vosjoli, P. de 1995. How to establish ornate Uromastyx. Vivarium (Lakeside) 7(3): 14-17, 52-53.
Wilms, T. 2007. Philbys Dornschwanzagame (Uromastyx ornata philbyi) - über eine fast unbekannte Schönheit. Draco 8(3) (31): 61-66.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W. 2000. Zur Taxonomie und Verbreitung der Arten der Uromastyx-ocellata-Gruppe (Sauria: Agamidae). Zoology in the Middle East 21: 55-76.
Wilms, T.; Mueller, H.D.; Loehr, B. 2002. Bunte Juwelen im Terrarium - Erfahrungen bei der langjährigen Pflege und Vermehrung von Uromastyx ornata (Heyden, 1827) bis zur F2-Generation. Draco 3(2) (10): 41-49.
Wilms, T.; Sindaco, R. 2012. Uromastyx ornata. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012: e.T198538A2531743. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T198538A2531743.en.
Zari, T.A. 1997. Food consumption of the herbivorous desert lizard, Uromastyx philbyi (Parker) (Reptilia: Agamidae). Egyptian Journal of Zoology 29: 185-193.
Zari, T.A. 1998. Effects of sexual condition on food consumption and temperature selection in the herbivorous desert lizard, Uromastyx philbyi. Journal of Arid Environments 38(3): 371-377.
Zari, T.A. 1999. On the reproductive biology of the herbivorous spiny-tailed agamid Uromastyx philbyi in western Saudi Arabia. Zoology in the Middle East 19: 123-130.
|
Uromastyx princeps
 |
Cherchi, M.A. 1954. Una nuova sotto-specie di Uromastix princeps O'Schaug. Atti della Societa Italiana di Scienze Naturali e del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano 93(3-4): 538-544.
Cherchi, M.A. 1958. Note su Uromastix princeps scorteccii Cherchi (Sauria). Atti. Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. 97: 107-111.
Gans, C. 1961. Lizards from Candala. Zoo Logic (Buffalo) 4(4): 3.
Ninni, E. 1933. L'Aporoscelis princeps (O'Schaug.) a Ras Hafun, Migiurtinia-Somalia Italiana. Natura (Milano) 24(3): 134-135.
Scortecci, G. 1933. Notizie e varieta. Osservazioni su di uno atrano agamide della Migiurtinia. Natura (Milano) 24(2): 92-97.
Scortecci, G. 1955. Viaggio di esplorazione biologica sulle montagne della Migiurtinia compiuto con il contribute del consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche. Bollettino dei Musei e degli Istituti Biologici dell'Universita di Genova 25 [1953-1955]: 43-105.
Scortecci, G. 1958. Esplorazione dello Ahl Mascat occidentale e centrale. Boll. Soc. Geogr. Ital. 4-5: 1-33.
|
Uromastyx shobraki
 |
Wilms, T. 2012. Uromastyx shobraki. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012: e.T199815A2612567. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T199815A2612567.en.
Wilms, T.; Böhme, W.; Wagner, P.; Lutzmann, N.; Schmitz, A. 2009. On the phylogeny and taxonomy of the genus Uromastyx Merrem, 1820 (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae: Uromastycinae) - resurrection of the genus Saara Gray, 1845. Bonner Zoologische Beiträge 56(1-2): 55-99.
Wilms, T.; Schmitz, A. 2007. A new polytypic species of the genus Uromastyx Merrem 1820 (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae: Leiolepidinae) from southwestern Arabia. Zootaxa 1394: 1-23.
|
Uromastyx thomasi
 |
Arnold, E.N. 1980. The scientific results of the Oman flora and fauna survey 1977 (Dhofar). The reptiles and amphibians of Dhofar, southern Arabia. Journal of Oman Studies Special Report 2: 273-332.
Hulbert, F.; Wilms, T. 1999. Arabia Felix. Auf der Suche nach Uromastyx thomasi im Sultanat von Oman. Reptilia (D) 4(16): 30-33.
Parker, H.W. 1930. Three new reptiles from southern Arabia. Annals and Magazine of Natural History (Ser. 10) 6: 594-598.
Wilms, T.; Al Rasbi, K.J.M. 2013. Uromastyx thomasi. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013: e.T199600A2605933. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T199600A2605933.en.
Wilms, T.; Loehr, B.; Hulbert, F. 2002. Erstmalige Nachzucht der Oman-Dornschwanzagame - Uromastyx thomasi Parker, 1930 - (Sauria: Agamidae: Leiolepidinae) mit Hinweisen zur intraspezifischen variabilitaet und zur Lebensweise. Salamandra 38(1): 45-62.
Zilger, H.J.; Grossmann, W. 2017. Titelbild: Uromastyx thomasi Parker, 1930. Sauria (Berlin) 39(2): 1-2.
|
Uromastyx yemenensis
 |
Wilms, T. 2012. Uromastyx yemenensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012: e.T199602A2606045. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T199602A2606045.en.
Wilms, T.; Schmitz, A. 2007. A new polytypic species of the genus Uromastyx Merrem 1820 (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae: Leiolepidinae) from southwestern Arabia. Zootaxa 1394: 1-23.
|
| | 





































































































































































































|

